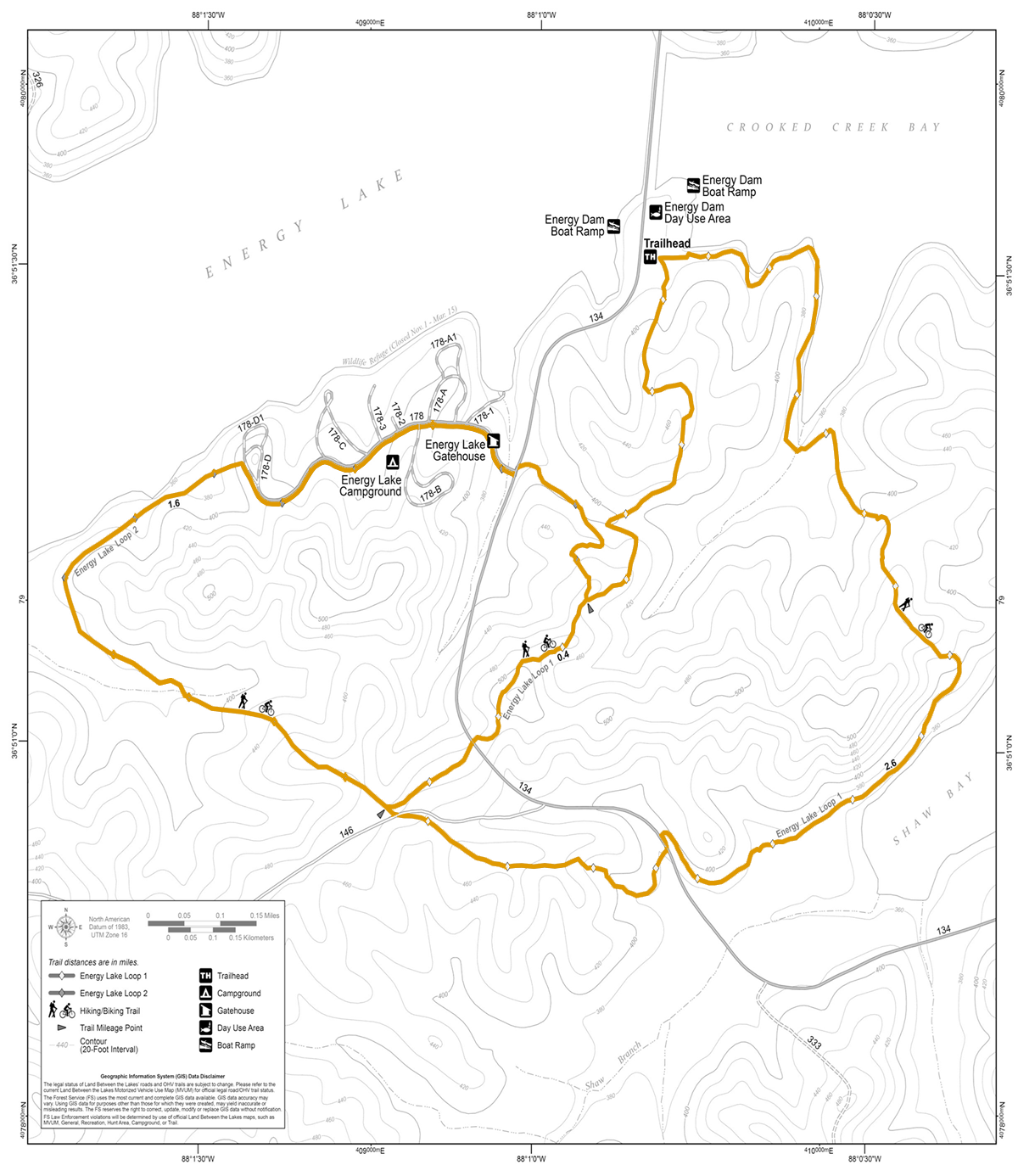
Homeplace 1850s Farm Map
Click markers below for location information.

Accessible Path
Front Field
While corn was king, tobacco served as an important cash crop as well. Farmers also planted other vegetables for resale. Yeoman farmers cultivated on average 40 acres of corn, earning enough income to make them middle class.
Living between the Cumberland and Tennessee Rivers and close to the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers impacted farm life here in Pryor Creek. These rivers provided easy access to send cash crops to urban markets.
Restrooms
Mule Pen & Pasture
 Weighing around 1,500 lbs., mules were the draft animal of choice for pulling heavy loads. All mules have a horse mother and Jack (donkey) father, making their offspring hardier and more disease and heat tolerant than horses.
Weighing around 1,500 lbs., mules were the draft animal of choice for pulling heavy loads. All mules have a horse mother and Jack (donkey) father, making their offspring hardier and more disease and heat tolerant than horses.
Double Pen House
 The most notable feature of this single family home is an open, central hallway that separates two equal sized “pens” or rooms. Families used one pen as living space, while the other pen – the parlor – welcomed visiting guests. The open central hallway faced the prevailing winds and served as a cool, shady setting for the family and guests.
The most notable feature of this single family home is an open, central hallway that separates two equal sized “pens” or rooms. Families used one pen as living space, while the other pen – the parlor – welcomed visiting guests. The open central hallway faced the prevailing winds and served as a cool, shady setting for the family and guests.
Smoke House
Laying away a supply of meat for the next year began shortly after the first frost. Dry salt curing preserved the meat, while the smoking process flavored it.
Wood Shed
Oxen pulled logs from surrounding forests to use for the fireplace and wood stove. Large logs were stacked outside, while stove wood stayed dry in the wood shed.
Vegetable Garden
Large gardens provided the main source of produce. Families ate fresh vegetables or preserved them for winter use. The nearby crib stores bean poles, hoes, and other garden tools. We plant heirloom seeds that date back from before the Civil War.
Corn Crib
Corn dominated southern agriculture in the 1850s. Corn not sold was stored on the cob for winter use for people and livestock.
Garden Crib
The crib stores bean poles, hoes, and other garden tools. We plant heirloom seeds that date back from before the Civil War.
Stock Barn with Breezeway and Loft
This barn has three stalls and a tack room for storing harnesses, saddles, and feed. The upper loft is for hay storage. Some of our livestock include rare and endangered breeds.
Spring
This was the water source for the original farm. The spring house was added for the museum and dismantled in 2015 in efforts to revive the spring. While we have been unable to bring back the spring, we are researching alternatives.
Single Pen House
Known as the “first generation” house, early settlers commonly built a one room or single “pen” log home. By mid-century, kitchens were added.
Ox Barn & Cribs
 This four-crib barn offers shelter for oxen. The two front cribs provide relief from summer heat and contain mangers for feeding. The loft stores hay and straw, and two back cribs store corn fodder.
This four-crib barn offers shelter for oxen. The two front cribs provide relief from summer heat and contain mangers for feeding. The loft stores hay and straw, and two back cribs store corn fodder.
Oxen are trained to work together with a yoke. Oxen typically weigh about 2,500lbs and do the heaviest farm work.
Blacksmith Shop
 Farms had small blacksmith shops to make or repair farm equipment. Common activities included creating nails, tools, and household items, sharpening plow points, repairing metal tools, and shaping horseshoes.
Farms had small blacksmith shops to make or repair farm equipment. Common activities included creating nails, tools, and household items, sharpening plow points, repairing metal tools, and shaping horseshoes.
Chicken House
 This log crib provides a safe haven for the chickens and ducks. At night, chickens sleep on the horizontal poles/roosts. Boxes on the left provide a safe place for the chickens to lay eggs.
This log crib provides a safe haven for the chickens and ducks. At night, chickens sleep on the horizontal poles/roosts. Boxes on the left provide a safe place for the chickens to lay eggs.
The ducks make nests and sleep on the ground; there they also lay their eggs. Our heritage breeds include Dominique Chickens and Black Cayuga Ducks.
Crop Field
While corn was king, tobacco served as an important cash crop as well. Farmers also planted other vegetables for resale. Yeoman farmers cultivated on average 40 acres of corn, earning enough income to make them middle class. Living between the Cumberland and Tennessee Rivers and close to the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers impacted farm life here in Pryor Creek. These rivers provided easy access to send cash crops to urban markets.
Tobacco Barn
Tobacco and corn served as cash crops in this region. Dark-fired tobacco’s name comes from the curing process. Farmers “fired” and “cured” this 13-month crop by building smoldering fires in floor trenches of the barn. It was the only commercial type raised here. By the 1860s, tobacco was a major cash crop in the area.
Hog Lot & Crib
 Typically hogs free ranged and foraged for acorns, chestnuts, and hickory nuts. In the fall, farmers placed hogs in enclosures like this one to fatten them up for the winter slaughter. Yeoman farmers helped make Tennessee the number one hog producer in the United States during the 1850s.
Typically hogs free ranged and foraged for acorns, chestnuts, and hickory nuts. In the fall, farmers placed hogs in enclosures like this one to fatten them up for the winter slaughter. Yeoman farmers helped make Tennessee the number one hog producer in the United States during the 1850s.
Tool Barn
 This barn provided sheltered workspace for farmers to build home furnishings and repair farm implements. Farmers stored tools and equipment in one of the tool barn “cribs” while plows, wagons, and buggies stayed under a barn lean-to or in a breezeway.
This barn provided sheltered workspace for farmers to build home furnishings and repair farm implements. Farmers stored tools and equipment in one of the tool barn “cribs” while plows, wagons, and buggies stayed under a barn lean-to or in a breezeway.
Build-A-Cabin Activity
Orchard
Every family would have an orchard to provide fruit on the table. Our orchard consists of a variety of heirloom fruit trees, including Bartlett pear, Horse apple, and Sheep Nose apple.